- Our Location
- #604 1087 2nd Ave NW CALGARY ALBERTA,
POSTAL CODE T2N 5B2 Canada
- working hours
- Mon - Fri : 9:00 Am - 5:00 Pm
- Our Location
- #604 1087 2ND AVE NW CALGARY ALBERTA,
POSTAL CODE T2N 5B2 CANADA
- working hours
- Mon - Fri : 9:00 Am - 5:00 Pm
Trigeminal Neuralgia: Introduction
The term Trigeminal Neuralgia (TN), has two words within it. Trigeminal nerve is one of the (twelve) cranial (head) nerves which has three divisions (ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular) supplying to the areas of upper eye-lid to the lower chin. Neuralgia means pain. TN is a disorder of the Trigeminal nerve which presents as facial pain and headache. The pain is characteristically severe, intense, sharp, episodic, periodical, excruciating, stabbing and short lasting.
Trigeminal Neuralgia is commonly misspelled as Trigeminal neuralgai, Trigeminla neuralgia, Trigemianl neuralgia, Trigmeinal neuralgia, Trigeminal euralgia.
Trigeminal nerve is the largest of twelve cranial nerves. All sensations from the face and mouth are covered by the Trigeminal nerve. One of the branches of the Trigeminal is often injected by your dentist while working on your dental cavity.
When the patient's Trigeminal nerve during an acute neuralgia phase was studied under electron microscope, it was revealed that the abnormality existed at the level of the inner nerve fibers called axons which carry nerve sensation, as well as the myelin (the nerve lining covering the nerve fibers). Due to the damage to such delicate parts, the nerve fiber behave like electrical wire with open ends, leading to electric shock like pain induced by touch or jerk.
What causes Trigeminal Neuralgia?
In short, it has been increasingly proved and understood that most cases of TN have demyelination of the sensory nerve fibers of the Trigeminal Nerve, either in the nerve root or (rarely) the brain stem. Demyelination means an erosion of the nerve sheath, which leads to the exposure of the nerve fibers. The exposed nerve fibers often get compressed or irritated by blood vessels (pulsating arteries or veins), which lead to painful episodes of Trigeminal Neuralgia due to misfiring of the nerve.
Trigeminal Neuralgia Causes: Factors Causing Trigeminal Neuralgia

01 Compression:
Abnormal compression of the nerve by an adjacent blood vessel in the brain
02 Demyelination:
Demyelination of the nerve that occurs as a result of nerve root injury
03 Nerve damage:
Physical damage to the nerve caused by dental or surgical procedures
04 Genetic tendency:
When we say genetic, it does not mean that every patient of TN has someone in the family having TN. Actually, there supposed to be a group of genes which are inherited and they evolve in certain way, when supported by other factors, leading to have TN. Only little understanding is achieved in this area, yet.
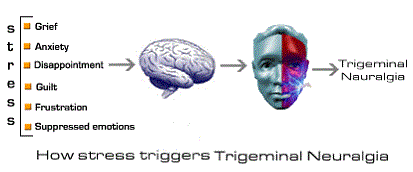
05 Stress & Trigeminal Neuralgia
Psychological stress is one of the triggering and aggravating factors if not primarily causative factor. It is a well-known fact that there is an inseparable bond between mind and body and that the psyche plays a vital role in maintaining health or causing diseases. It is a common experience in clinical practice that some patients report the onset of trigeminal neuralgia following major stressful events like divorce, death of close relatives, change of job, unhealthy family relationships, etc and this perception of patients that psychological stress can worsen trigeminal neuralgia has been supported in clinical studies. It is a common experience of many patients to have sudden pain when they are emotionally charged.
Stress has been identified as an important cause in triggering as well as maintaining trigeminal neuralgia especially in the chronic cases. Stress can be in the form of:
- Prolonged anxiety due to any cause
- Grief, depression
- Suppressed anger/emotions
- Guilt
- Frustrations
- Despair
- Disappointments in life
- Nervous temperament
- Failures in business, etc.
Frustration due to the unexplainable nature of the disease only makes the matters worse for the patient. Not all cases have a clear-cut cause and in many cases the cause may remain obscure i.e. idiopathic.
06 Tumor and Multiple Sclerosis
Trigeminal Neuralgia pain caused due to tumor is called as secondary trigeminal neuralgia. Multiple sclerosis hardly contribute as the factor for causing Trigeminal Neuralgia.
07 Immunological factors:
Certain immunological parameters are found to be affecting TN in different ways. Immunity is now considered to be an important factor for pain and TN. Also, immunity is controlled and affected by emotional (stress) factors as well as genetic factors.
Multiple Causes of Trigeminal Neuralgia:
It has been observed that TN often is backed by more than one causes. As one can see, immunological causes are supported by stress and genetic factors; suggesting the causative factors work in a chain and they are interconnected.
Factors governing Pain and seizure threshold:
Episodes of trigeminal neuralgia increase when the patients pain threshold gets lowered. The pain threshold is affected by several known and unknown factors, some of them are:
- Stress
- Exposure of cold wind
- Brain trauma
- Inadequate sleep
- Poisoning with lead or other chemicals
- Hormonal fluctuation before and after the menses
- Hyperglycemia (High blood sugar)
- Certain antibiotics and anesthetic agents
Symptoms of Trigeminal Neuralgia (TN)
As Trigeminal Neuralgia is typically described by the patients as episodes of extremely severe pain. TN is probably the most painful condition known to the human race.
The Trigeminal Neuralgia pain is described as:
a Lancinating pain (as if poked by thorns)
b Like electric shock (as if a live wire is left free inside of the face)
c Stabbing pain
d Excruciating pain (as if a drilling machine is put on the certain part of face)
e Stitching pain
f Shooting pain
g Burning (as if fire)
The Trigeminal Neuralgia pain may appear suddenly, may last for a fraction of second or may be for a few minutes. The pain is periodic in nature. In rare cases it may last for a couple of hours, making the patients almost immobile, whereby he or she may not be able to do any other activity. One would tend to hold the affected part until pain settles. Some patients may feel frustrated and and may think of committing suicide out of hopelessness.
The pain might typically get worse by following triggers:
a Chewing and drinking
b Brushing and gargling
c Touching the face
d Talking
e Kissing
f Slightest wind or draft of air
g Movement of eye lids or blinking
The Trigeminal Neuralgia is more common in the age group of 40 years plus. However, younger people as well as children may also present with TN. Very uncommon in children. The pain may get triggered either without any cause or by certain motions involving the facial muscles, such as washing face, brushing teeth, gargling, shaving, applying facial make-up, touching the face, blowing, kissing, etc. The pain may initiate in any of the parts supplied by the Trigeminal nerve. However, it may vary from patient to patient depending on which of the three divisions of the Trigeminal nerve is affected. It may present with pain in the head, upper face, cheeks, dental pain, pain in lips, side of tongue, chin, etc. In some cases the pain may present as dull aching, burning, constant pain. Usually, one of the sides (right or left) is affected. The cause: The exact cause of TN remains a mystery. It is observed to run in families, indicating genetic predisposition. Detailed case study in our practice has shown history of prolonged stress in many cases. Prolonged underlying anxiety with the background of genetic diathesis may make one prone to this painful condition.
ORDER TREATMENT ONLINE
Our Homeopathy treatment is now just a few clicks away.
(Treatment for additional diseases charged at 50%)

 Find
out the chances
Find
out the chances
of cure (Free)

